Water treatment is essential for providing clean and safe water for various uses, including drinking, industrial processes, and wastewater management. Tube settlers, also known as inclined lamella clarifier media, play a important role in enhancing the sedimentation process in water treatment.This comprehensive guide will delve into the concept of tube settlers, their benefits, applications, and the technology behind them.
1. What is Tube Settler?
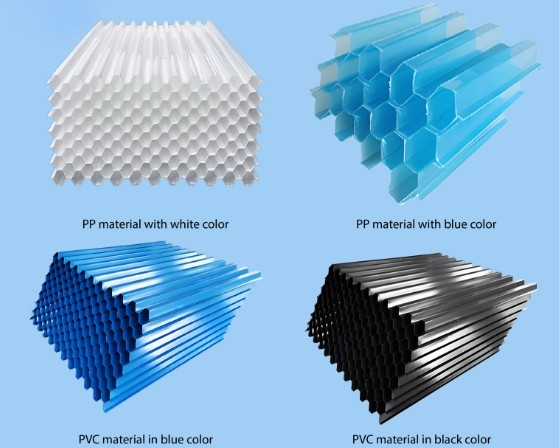
A tube settler, also known as a lamella clarifier or inclined plate settler media, is a water treatment device designed to enhance the sedimentation process by increasing the effective settling area. It consists of a series of closely spaced, inclined tubes or plates arranged in parallel. These tubes or plates create multiple settling surfaces, allowing suspended particles to settle out of the water more efficiently.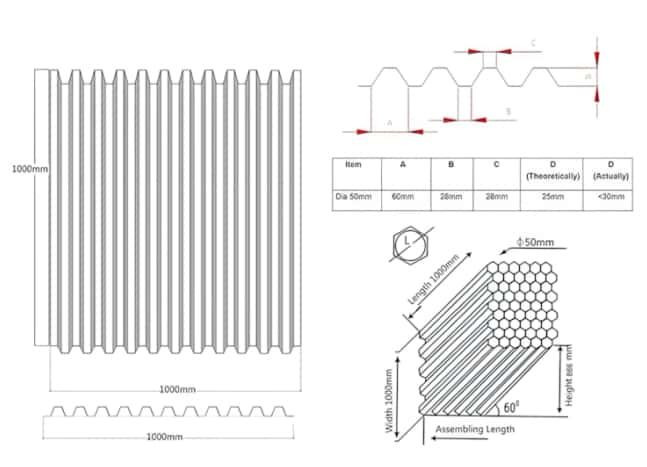
Specifications:
2.How Do Tube Settlers Work?
Sedimentation is a process where gravity is used to remove suspended solids from water. The efficiency of this process depends on factors like particle size, density, and water flow rate.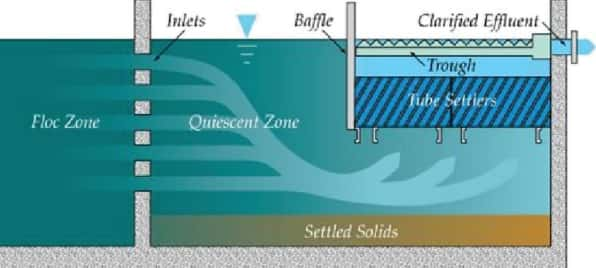 Tube settlers work on the principle of shallow-depth sedimentation. As water flows upward through the inclined tubes, particles settle onto the surface of the tubes and slide down into a collection area. This configuration increases the effective settling area without requiring a larger footprint for the settling tank. The key advantages of this design include:
Tube settlers work on the principle of shallow-depth sedimentation. As water flows upward through the inclined tubes, particles settle onto the surface of the tubes and slide down into a collection area. This configuration increases the effective settling area without requiring a larger footprint for the settling tank. The key advantages of this design include:
- 2.1 Increased Settling Efficiency: The inclined tubes provide a greater surface area for particles to settle, enhancing the removal of suspended solids.
- 2.2 Reduced Footprint: Tube settlers can achieve the same or better performance as traditional sedimentation tanks but with a smaller footprint, making them ideal for space-constrained facilities.
- 2.3 Improved Water Quality: By removing more suspended solids, tube settlers contribute to better water clarity and overall quality.
- ( video made by Parkson Corporation )
3.Design and Manufacturing of Tube Settler
3.1 Design Parameters and Considerations
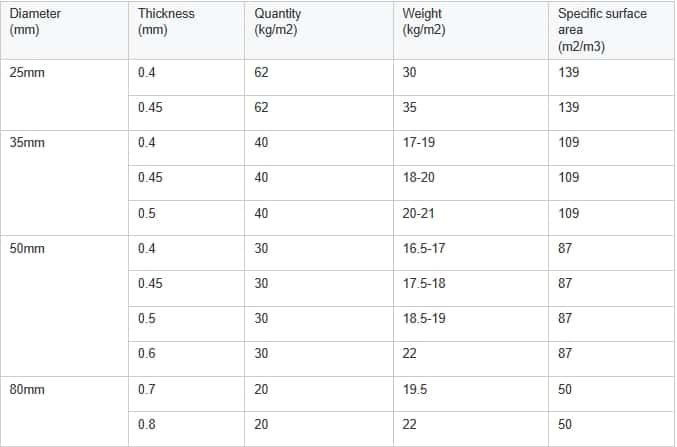
Key design parameters include the inclination angle of the tubes, tube length, tube diameter, and spacing between tubes. These factors influence the settling efficiency and overall performance of the tube settlers.
3.2 Material Selection
Materials used for tube settlers must be durable, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for the specific water chemistry. Common materials include PVC, stainless steel, and fiberglass.
3.3 Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Manufacturing tube settlers involves processes like cutting, molding, and assembling the components. Advanced techniques ensure precision and quality in the final product
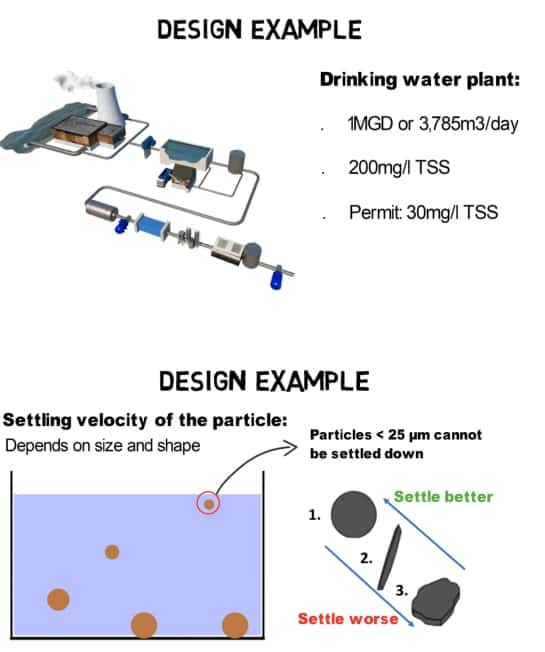
4. Tube Settler Design Example
Plant Specifications
- Maximum Flow: 1 million gallons per day (MGD) or 3,785 cubic meters per day (m³/day).
- Influent Suspended Solids: 200 mg/L.
- ffluent Permit Requirement: 30 mg/L.
 Determining Settling Velocity
Determining Settling Velocity
The settling velocity of particles is influenced by their size and shape. Smaller particles tend to settle slower due to lower settling velocities. Particles less than 25 micrometers typically do not settle effectively due to turbulence and drag forces.
Stokes' Law
Stokes' law is used to calculate the settling velocity of particles under laminar flow conditions
vs = (ρp - ρf) * d² * g / (18 * μ
Where:
vs = settling velocity
ρp = density of the particle
ρf = density of the fluid
d = diameter of the particle
g = gravitational acceleration
μ = dynamic viscosity of the fluid
Example Calculation
For sand and gravel particles:
Minimum Particle Size: 50 micrometers.
Density Difference: 12.5 lbs/ft³ or 200 kg/m³.、
Form Factor: 0.8 for rounded particles.
Settling Velocity: 1.67 m/h (calculated).
Applying Safety Factor
To ensure effective design, a safety factor is applied to account for variations in flow and particle interactions. In this example, a safety factor of 2 is used:
Adjusted Settling Velocity = 1.67 m/h / 2 = 0.835 m/h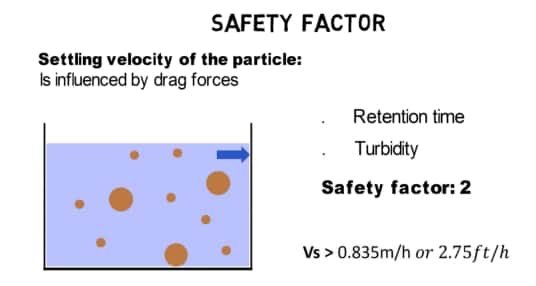 Calculating Tube Settler Requirements
Calculating Tube Settler Requirements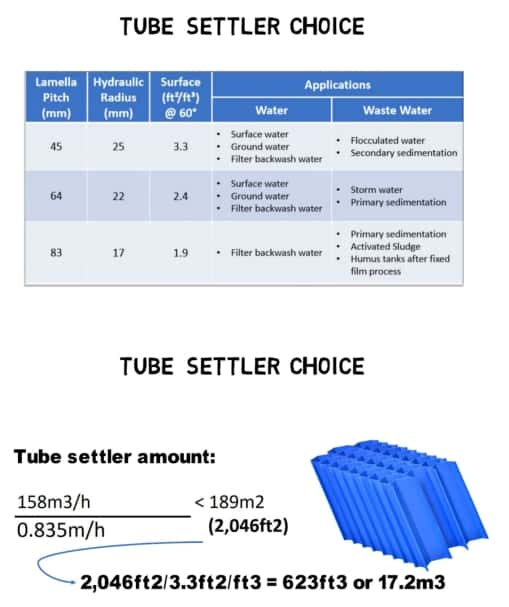 Using the LS50 tube settler design with a channel distance of 45 mm and a projected surface area of 3.3 to 3.5 ft²/ft³
Using the LS50 tube settler design with a channel distance of 45 mm and a projected surface area of 3.3 to 3.5 ft²/ft³
1. Total Projected Surface Area Required:
Total Surface Area = Flow Rate / Adjusted Settling Velocity
Total Surface Area = 3,785 m³/day / 0.835 m/h = 189 m
2. Volume of Tube Settlers Needed:
Volume = Total Surface Area / Projected Surface Area per Volume
Volume = 189 m² / 11 m²/m³ = 17.2 m³
Summary
In this example, the drinking water plant would need approximately 17.2 cubic meters of LS50 tube settlers to effectively remove sand and gravel particles, meeting the effluent permit requirements
Tube settlers significantly enhance the settling process by increasing the effective settling surface area, allowing for efficient sediment removal and improved water quality
5. Applications of Tube Settlers
Tube settlers find applications in a wide range of water and wastewater treatment processes, including:
5.1 Drinking Water Treatment: Enhancing the sedimentation process to produce clear and safe drinking water.
- 5.2 Wastewater Treatment: Improving the removal of suspended solids in primary and secondary treatment stages.
- 5.3 Industrial Water Treatment: Treating process water in industries such as mining, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
- 5.4 Stormwater Management: Reducing the sediment load in stormwater runoff before it enters natural water bodies.

6.Tube Settlers VS Plate Settlers
The sedimentation process is a critical component in both water and wastewater treatment. This process leverages gravity to settle and remove suspended solids. Advanced settling techniques employ lamella, commonly referred to as tube settlers or plate settlers, to minimize the vertical distance solids must fall to reach a "settling surface." Both tube settlers and plate settlers enhance flow rates, improve effluent quality, and allow for more compact sedimentation basins. Despite their shared principles, there are significant differences between these two technologies

Characteristics of Tube Settlers and Plate Settlers
Tube Settlers:
- Utilize multiple adjacent tubular channels sloped at a 60° angle.
- Tubular channels' size and shape vary by manufacturer.
- Tube settler design features trapezoidal shapes created by thermoforming PVC sheets.
Plate Settlers:
- Consist of a series of inclined plates typically made of steel.
- Plates are spaced two to three inches apart on a 55° to 60° angle.
- Design results in different application rates compared to tube settlers.
Comparing Design Parameters
The application rate (flow rate/coverage area in gpm/ft²) differs between tube and plate settlers due to varying effective settling areas. For a direct comparison, tube settler application rates can be converted to an equivalent “plate” application rate, factoring in the projected surface area of tubes.
Design Parameter Comparison Table:
Angle of Inclination | 60° | 55° to 60° |
Material | PVC | Steel |
Installation | Lightweight, easy to install | Requires heavy lifting equipment |
Capital Cost | Lower | Higher |
Depth Limitation | Suitable for shallow tanks | Less limitation on depth |
Lifespan | 20-25 years with maintenance | Longer due to material construction |
Risk of Corrosion | Low | Higher in certain environments |
UV Protection | Requires UV protection | Not typically required |

Tube Settler Analysis
Advantages:
Lightweight PVC allows for easy installation without heavy lifting equipment.
Lower capital cost due to construction materials.
Suitable for shallow tanks with underflow velocity concerns.
Long service life of 20-25 years with proper maintenance.
Only PVC tube settlers need replacement at the end of their useful life.
Strong enough to walk on for maintenance purposes.
Customizable to fit various basin configurations.
Disadvantages:
Maximum module vertical height is 41 inches, limiting the application rate to 3.5 gpm/ft².
PVC requires protection from extensive UV exposure. Zhongxing tube settlers include UV inhibitors, and protective surface grating is available for additional protection.
Plate Settler Analysis
Advantages:
Less depth limitation, suitable for deeper basins.
Longer lifespan due to robust material construction.
Disadvantages:
Higher capital cost, often two to three times more than tube settlers.
Higher installation costs due to the need for heavy lifting equipment.
Requires deeper basins to accommodate underflow velocities.
Risk of corrosion in certain industrial wastewater environments.
Choosing between tube settlers and plate settlers depends on specific project requirements, including budget, basin depth, and maintenance capabilities. Tube settlers offer cost efficiency and ease of installation, making them ideal for shallow tanks. Plate settlers, on the other hand, provide durability and are better suited for deeper basins despite higher costs and installation complexity
7. tube settler's Installation
Installing a tube settler requires following a series of detailed steps to ensure its functionality and overall system stability. Here are the detailed installation steps

Preparation
Site Survey and Preparation
1.Confirm the dimensions of the installation site to ensure adequate space for installation and maintenance.
2.Clear the site to ensure it is free from debris and obstacles.
Tools and Materials Preparation:
1.Prepare necessary tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, levels, etc.
2.Prepare the materials needed for installation, such as tube settler components, brackets, bolts, etc.
Installation Steps
1. Bracket Installation:
1.Determine the installation position and height of the brackets according to the design drawings.
2.Use expansion bolts or chemical anchors to secure the brackets to the inner wall of the sedimentation tank or other supporting structures, ensuring the brackets are level and stable.
2. Tube Settler Component Installation:
1.Transport the tube settler components to the installation location carefully to avoid damage.
2.Follow the manufacturer’s installation manual to connect the tube settler modules one by one, ensuring tight and leak-proof connections.
3. Module Fixation:
1.Install the connected tube settler modules onto the brackets, ensuring the modules are securely fixed to the brackets.
2.Use bolts or other fasteners to secure the modules to the brackets, using lock nuts or washers if necessary
4. Adjustment and Calibration:
1.Use a level to check the levelness of the tube settler, ensuring it is placed horizontally to ensure sedimentation efficiency.
2.Adjust the angle and position of the tube settler as per the design requirements to ensure optimal water flow path and sedimentation efficiency
5. Connecting Pipes:
1.Connect the inlet and outlet pipes to the tube settler according to the design drawings, ensuring secure and leak-proof connections.
2.Install necessary valves and flow meters to control and monitor the water flow
6. Inspection and Testing:
1.Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the entire system to ensure all connections are secure and leak-proof.
2.Perform a trial run to check water flow and sedimentation efficiency, ensuring the system operates normally
7. Recording and Maintenance:
1.Record key data and parameters during the installation process for future maintenance and management.
2.Regularly inspect and maintain the tube settler to ensure long-term stable operation.
Precautions
Safety Measures: Ensure construction personnel wear necessary protective gear such as safety helmets and gloves during installation.
Environmental Protection: Ensure waste and debris generated during installation are promptly cleaned up to avoid environmental pollution.
By following these steps, you can successfully install a tube settler and ensure its efficient operation. For more detailed technical guidance, refer to the manufacturer’s installation manual or seek professional technical support.
8. Summary
In conclusion, tube settlers offer a robust, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for modern water treatment challenges. Their ability to enhance sedimentation, reduce operational costs, and promote sustainability makes them a valuable asset in achieving high-quality water treatment standards. Water treatment facilities that adopt tube settler technology can expect improved performance, reduced costs, and a positive environmental impact, ultimately contributing to the goal of providing safe and clean water for communities worldwide.

We are a leading manufacturer of high-quality tube settlers, committed to providing innovative and efficient solutions for your water treatment needs. With extensive experience and expertise, we offer customizable tube settler systems tailored to meet the unique requirements of our clients. We welcome inquiries from both domestic and international customers and are dedicated to delivering superior products and exceptional service. Partner with us to enhance your water treatment processes and achieve optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our tube settler technology can benefit your operations