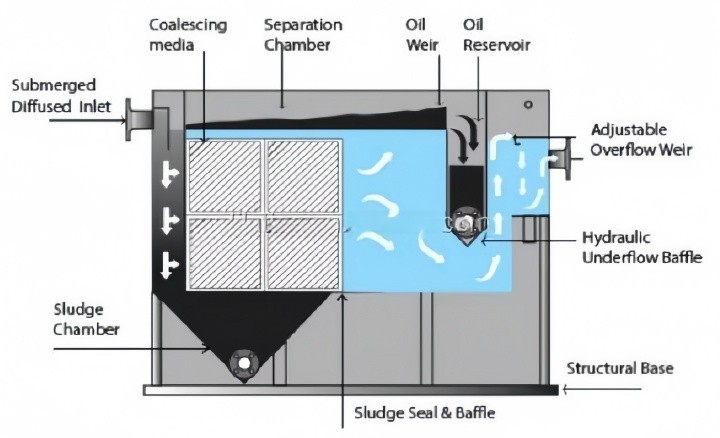
In industries where precision in fluid handling is paramount, coalescing media plays a vital role in ensuring effective separation and purification processes. Coalescing media refers to specially engineered materials that aid in merging and separating liquids or aerosols from gas or other liquid mixtures. This technology is commonly applied in various fields—from oil-water separation in wastewater management to mist elimination in gas processing and air purification. Its effectiveness in improving fluid quality and enhancing system efficiency has made it indispensable in meeting both operational demands and environmental regulations.
As industries evolve to prioritize cleaner, more sustainable operations, coalescing media has emerged as a key solution for fluid management. This article delves into the diverse types of coalescing media, exploring its functions, applications, benefits, challenges, and recent technological advancements. Additionally, we examine the environmental impact and future prospects of coalescing technologies in an industrial landscape where the need for clean, efficient fluid handling systems is ever-growing.
1. What is Coalescing Media?
Definition
Coalescing media is a type of material specially designed to capture and merge (or “coalesce”) fine droplets or particles from a fluid mixture, allowing for the separation of one substance from another. It operates on the principle of bringing small particles or droplets together to form larger ones, which can then be removed from the mixture. This mechanism is essential in industries where precision separation is critical, whether in purifying gases, separating immiscible liquids, or eliminating contaminants.

Purpose
The main purpose of coalescing media is to enhance the efficiency and purity of fluid separation processes. In applications like gas purification, water treatment, or oil separation, coalescing media captures unwanted particles or droplets, forming larger clusters that can be separated from the main fluid. By facilitating the removal of contaminants and ensuring cleaner outputs, coalescing media supports improved product quality, enhanced system longevity, and increased environmental compliance.
Mechanism
Coalescing media operates through a combination of physical and mechanical forces. When fluid flows through the media, the small particles or droplets come into contact with the fibers or surfaces within the media. Here, they accumulate and merge with other droplets, forming larger ones. Once they reach a critical size, these droplets become heavy enough to be separated through gravitational settling, filtration, or other means.
Depending on the specific type and application, coalescing media can be engineered with various materials, including glass fibers, polyesters, or polypropylene, each tailored to suit the chemical properties of the target fluid and environmental conditions. This unique mechanism of action makes coalescing media highly adaptable across a range of applications, from removing mist in gas processing to separating oil from water in industrial wastewater treatment.
2. Types of Coalescing Media
Coalescing media comes in various types, each designed to cater to specific applications and fluid separation needs. The main types include Mist Eliminators (Gas-Liquid Coalescers), Coalescing Filters, Liquid-Liquid Coalescers (Oil-Water Separators), and Air-Oil Separators. Each type is structured to address unique challenges in separating fluids, whether in removing mist, separating liquid droplets, or ensuring the purity of gases.
Mist Eliminators (Gas-Liquid Coalescers)
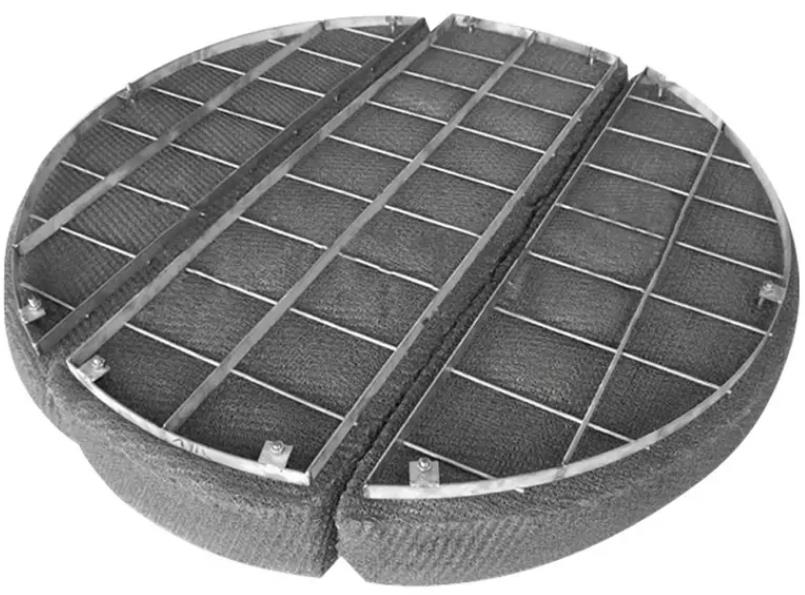

Mist eliminators, also known as gas-liquid coalescers, are used to capture and separate fine liquid droplets from a gas stream. This type of coalescing media is essential in industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas processing, and chemical manufacturing. In these fields, mist eliminators improve the purity of gases by removing liquid droplets that could interfere with downstream processes or damage equipment. These coalescers are usually made of layered fibers or meshes that force the liquid droplets to coalesce, allowing gravity to pull them out of the gas stream.
Coalescing Filters
Coalescing filters are widely used to purify gases and liquids, capturing unwanted liquid droplets or aerosols in the process. They are commonly found in compressed air systems, HVAC applications, and industrial gas production. For example, in air purification, coalescing filters remove oils, water vapor, and other contaminants from compressed air, ensuring that the resulting gas is clean and dry. The filter material, typically composed of fine fibers like borosilicate glass, enables it to capture very small particles and droplets, enhancing air and gas quality across a variety of applications.
Liquid-Liquid Coalescers (Oil-Water Separators)
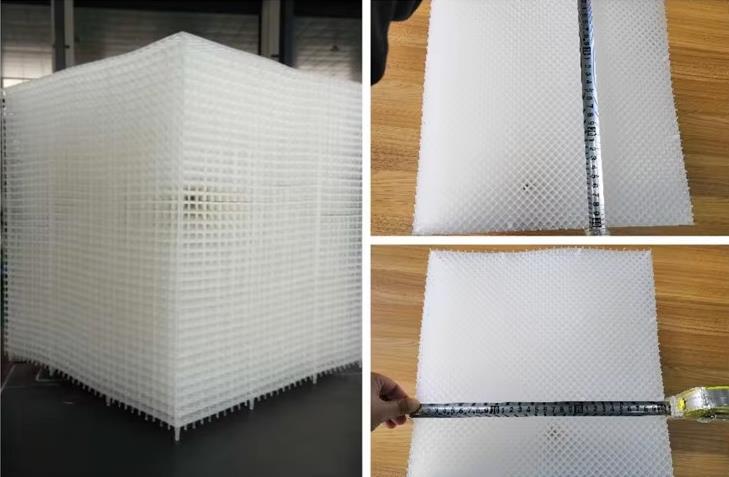
Designed specifically to separate immiscible liquids, liquid-liquid coalescers are often applied in situations where oil needs to be removed from water, such as in wastewater treatment or oil extraction processes. In these cases, the coalescing media captures tiny droplets of oil within the water, allowing them to merge into larger droplets that float to the surface. Oil-water separators are a critical component in industries with stringent environmental regulations, as they ensure that effluents are treated before being discharged. This kind product include HD Qpac packing, drift eliminator etc.

Air-Oil Separators
In compressed air systems, air-oil separators are essential for capturing oil droplets from compressed air, thereby preventing oil contamination in equipment. They are common in applications involving air compressors, where they filter out any trace oils, allowing only clean air to pass through. This not only ensures the purity of the compressed air but also extends the life of the equipment by preventing oil buildup and mechanical wear. These separators typically utilize a fibrous coalescing media that can effectively trap and separate oil droplets.

3. Applications of Coalescing Media
The versatility of coalescing media allows it to be applied across numerous industries, each leveraging its separation and purification benefits.
Oil & Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, coalescing media is used extensively for separating liquids from gas streams and removing contaminants in processes like natural gas dehydration, pipeline maintenance, and refining. Mist eliminators, for example, help remove liquid hydrocarbons from natural gas, enhancing fuel quality and protecting pipeline infrastructure. Additionally, liquid-liquid coalescers are used to separate oil from water during drilling and refining, meeting regulatory standards for effluent discharge.
Water Treatment
Water treatment facilities rely on coalescing media, particularly oil-water separators, to remove oil and other contaminants from wastewater. This is crucial in facilities handling industrial discharge, where oil-water separation ensures that the treated water meets environmental regulations before being released. Coalescing media used in these applications often include hydrophobic materials that can efficiently separate oil from water, allowing cleaner water to be processed and released.
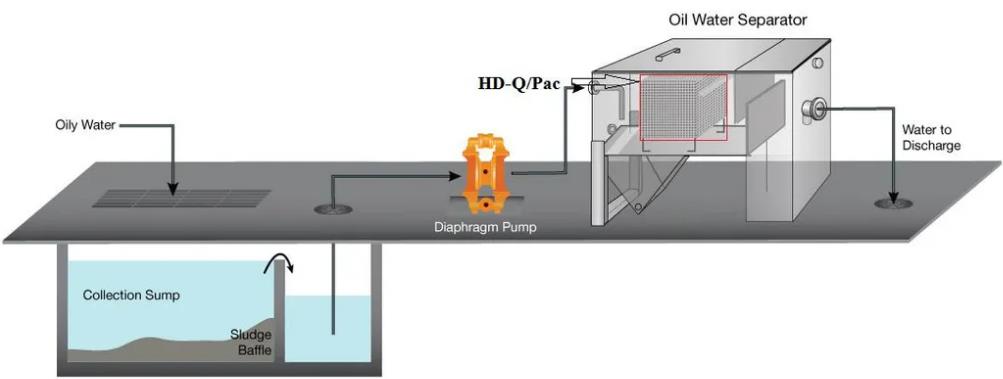
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, coalescing media is widely used in compressed air systems, HVAC applications, and chemical production. For example, coalescing filters are deployed in air purification systems to ensure that compressed air used in manufacturing is free from contaminants like water vapor, oils, and particles. This not only protects machinery from damage but also enhances product quality by ensuring clean air in processes where even minor impurities could affect the end product.
Pharmaceutical and Food Processing
The pharmaceutical and food processing industries have stringent standards for cleanliness and contamination control. Coalescing media plays a critical role in air and fluid purification in these sectors, ensuring that air systems and production environments are free of contaminants. In these applications, coalescing filters are often used to capture particles and aerosols that could compromise product quality or safety. By maintaining clean air and fluid standards, coalescing media helps these industries adhere to health and safety regulations.
Aerospace and Automotive
In aerospace and automotive applications, coalescing media is crucial for fluid separation in hydraulic and fuel systems. In aircraft, for instance, it ensures that fuel and hydraulic fluids are free from contaminants, thus enhancing system reliability and reducing maintenance needs. In automotive applications, coalescing media is used in air-oil separators within engine systems to prevent oil contamination, ensuring cleaner emissions and protecting engine components.
4. Benefits of Using Coalescing Media
Coalescing media provides a range of benefits that make it indispensable for fluid separation and purification across industries. These advantages include improved separation efficiency, environmental compliance, cost savings, and adaptability to various applications.
Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of coalescing media is its high separation efficiency, which enables industries to achieve higher purity and quality of fluids. By merging and removing fine droplets and particles, coalescing media improves the effectiveness of separation processes, allowing systems to operate with cleaner inputs and outputs. This increased efficiency not only enhances fluid quality but also contributes to the overall productivity of the industrial systems that depend on purified gases, liquids, and emulsions.
Environmental Compliance
Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly strict, especially in sectors like oil and gas, manufacturing, and wastewater treatment. Coalescing media plays a significant role in helping industries meet these standards by ensuring that pollutants and contaminants are removed from fluids before they are released into the environment. Oil-water separators, for instance, prevent oil from being discharged into water bodies, which helps companies avoid fines and align with environmental mandates. By enabling compliance, coalescing media supports industries in adopting environmentally responsible practices.
Cost-Effectiveness
Using coalescing media can result in significant cost savings. Improved separation efficiency reduces the need for repeated filtering or processing cycles, thereby conserving energy and lowering operational costs. In addition, by removing contaminants that could otherwise damage equipment, coalescing media reduces maintenance requirements and extends the lifespan of industrial systems. This reduction in maintenance needs and prolongation of equipment life leads to substantial savings in both direct and indirect costs, making coalescing media a cost-effective solution for many industries.
Versatility
The versatility of coalescing media allows it to adapt to a wide range of applications, from removing mist in gas processing to separating oil from water in wastewater treatment. Coalescing media can be engineered with various materials, shapes, and configurations to meet specific separation needs. This adaptability makes it suitable for use across different industries, ensuring consistent performance in diverse environments and under varying operational conditions. Its flexibility ensures that it can be customized to handle different fluid types, chemical compositions, and separation requirements.
5. Challenges in Coalescing Media Technology
While coalescing media offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges. These include issues related to clogging, efficiency degradation, material compatibility, and environmental concerns associated with used media disposal.
Clogging and Maintenance
One of the most common challenges with coalescing media is clogging. Over time, contaminants and particles accumulate within the media, which can lead to blockages. When clogging occurs, the separation efficiency drops, and the system requires more frequent maintenance to restore optimal performance. This regular maintenance can be costly and time-consuming, particularly in high-throughput systems or environments with high levels of contamination. Some industries are exploring self-cleaning coalescing media to address this issue, though these technologies are still in the developmental stage.
Efficiency Degradation
Another challenge is that certain coalescing media materials can degrade over time, especially when exposed to harsh chemicals, high temperatures, or corrosive fluids. This degradation can result in a gradual decline in separation efficiency, affecting the overall performance of the system. Industries that operate in extreme conditions may require specially designed coalescing media to withstand these environments, but these materials are often more expensive and may still need frequent replacement.
Limited Compatibility
Certain types of coalescing media are not compatible with all fluid types or environments. For instance, while some materials are ideal for water separation due to their hydrophobic properties, they may not perform as well in high-temperature or chemically aggressive settings. This limited compatibility can restrict the application of certain coalescing media, requiring industries to carefully select the type of media that matches their specific operational needs. Finding compatible materials that can balance performance with durability remains a challenge, particularly for industries with diverse separation requirements.
Environmental Concerns
The disposal of used coalescing media poses environmental challenges, particularly in applications where the media becomes saturated with hazardous substances like oil or industrial chemicals. These contaminated media require proper handling and disposal to avoid environmental contamination. In response to this issue, some industries are exploring recyclable or biodegradable coalescing media options to reduce environmental impact. However, these alternatives are not yet widely available, and their adoption is limited by higher costs and technical limitations.
Conclusion
Coalescing media has proven itself to be an indispensable tool for fluid separation and purification, delivering significant benefits across various industries. From improving separation efficiency and ensuring regulatory compliance to reducing environmental impact, coalescing media supports cleaner, more effective fluid management. Technological advancements, such as nano-coalescing materials, hybrid media, self-cleaning systems, and smart coalescing media, demonstrate the potential of coalescing media to meet the evolving needs of modern industries.
In a world where clean and efficient fluid handling is becoming increasingly essential, coalescing media is poised to make a lasting impact. As industries embrace more sustainable practices, coalescing media will remain at the forefront, contributing to a cleaner and more resource-efficient future.